一个boot程序(2)
前面写的boot程序仅仅是在屏幕上不停的打印一个字符串,而boot程序真正的作用是将loader程序载入到内存执行。这篇note会完成这这部分的工作。
boot和loader通常被放在一起成为bootloader,但由于引导介质的限制,boot往往只执行相对简单的任务,后续的各种工作都有loader来完成。
FAT12 文件系统
为了实现足够的简单,这里使用FAT12文件系统来装载loader程序。
引导扇区
FAT12的引导扇区位于开始的512字节(第0扇区),大多数参数使用默认值即可:
; 实际上变量的名字无所谓,但大小必须满足FAT12引导扇区的规定,下面的变量必须放在偏移量为3的地方,前3个字节用来存跳转指令
; 跳转到偏移量为62的地址
oem_name db "serenity" ; 8 bytes
bytes_per_sector dw 512 ; 2 bytes,所以用double word
sector_per_cluster db 1 ; 1 byte
reserved_sector_count dw 1 ; 2 bytes
num_of_fats db 2 ; 1 bytes
root_entry_count dw 224
total_sectors_16 dw 2880
media db 0xf0
sector_per_fat dw 9
sector_per_track dw 18
num_of_head dw 2 ; 磁头数
hidden_sector dd 0 ; 4 bytes
total_sectors_32 dd 0 ; 如果 totoal_sectors_16 为0 就用这个
drive_number db 0 ; bios 中断调用需要的驱动器号
reseved db 0
boot_signature db 0x29
volume_id dd 0
volume_label db "boot-loader" ; 11 bytes
filesystem_type db "F A T 12" ; 8 bytes whatever
; offset 62, length 448
bootloader_code_start:
; 引导代码放在这里,长度不超过448字节
times 510 - ($ - $$) db 0 ; 引导代码不到448用来填0 padding,
dw 0xaa55 ;引导扇区标识
软盘结构
1.44MB软盘大概长这个样子
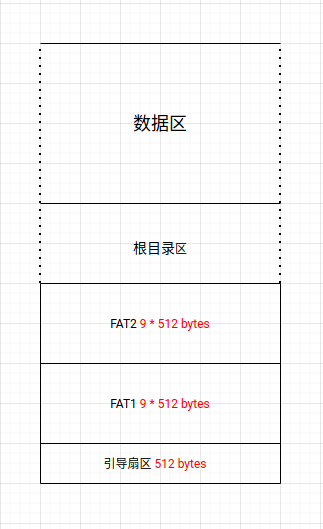
引导扇区占1个扇区,FAT1和FAT2各占9个扇区之后是根目录区和数据区。
FAT表的表项和数据区的簇号是一一对应的, 由于FAT表项的0和1项已经用了(历史原因)所以数据区的第一个有效簇号是2,即下面的目录项结构中的first_cluster是从2开始的:
struct Dir
{
char name[11]; // filename 8 bytes + extension 3 bytes
char attr; // 1 byte, file attribute, file or folder ?
char reserved[10]; // 10 bytes
short last_write_time; // 2 bytes
short last_write_date; // 2 bytes
short first_cluster; // 2 bytes
int file_size; // 4 bytes
}
总共 11 + 1 + 10 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 4 = 32字节
修改boot程序
之前的boot程序仅仅打印hello world,这里我们要将boot程序放到软盘的引导扇区的引导代码处,它将在FAT12文件系统中查找loader程序并加载loader,loader程序后面会写,这里只需要知道loader程序会拷贝到FAT12文件系统中,而boot程序需要找到并加载它。
要做的事情很简单:
- 1. 遍历根目录,找到文件名为设定的loader名字(比如loader.bin)
- 2. 如果找到,加载这个文件
- 3. 如果没找到,显示错误然后死循环(
jmp $)即可
然而,问题是整个程序只能使用汇编,并且只能通过BIOS中断服务来操作FAT12文件系统以及代码长度限制在448字节,因此代码组织相当重要。
封装读取一个扇区函数
刚开始就遇到了问题,前面说的扇区号是LBA(Logical Block Address)而BIOS中断服务int 13h, ah = 02h接收的是CHS(Cylinder Head Sector),因此需要将LBA转成CHS。LBA转为CHS需要用到前面定义的变量num_of_head和sector_per_track 关系如下:
Sector = LBA % sector_per_track + 1
Head = LBA / sector_per_track % num_of_head
Cylinder = LBA / sector_per_track / num_of_head
由于前面设定(软盘)中num_of_head为2,因此上面的式子还可以写成
Head = (LBA/sector_per_track) & 1
Clyinder = (LBA/sector_per_track) >> 1
按照BIOS中断int 13h, ah=0ah的要求,可以写出读取一个扇区的函数:
; Sector = LBA % sector_per_track + 1
; Head = (LBA/sector_per_track) & 1
; Cylinder = (LBA/sector_per_track) >> 1
; read_cl_sector(di, cl, [es:bx]) where bx is set to 5000h (assume loader size if less thand 5000h so won't overlap with 64k boundary)
read_n_sector: ; where n is cl
push di ; save LBA
push bp
mov bp, sp
sub sp, 2
mov byte [bp-2], cl ; save cl
mov ax, di
mov cl, [sector_per_track]
div cl ; quotient in al, residual in ah
; set sector
inc ah
mov cl, ah
; set head
mov dh, al
and dh, 1
; set cylinder
mov ch, al
shr ch
mov dl, [drive_number]
; when error occurred CF will be set
try_again:
mov ah, 02h ; int 13h arg
mov al, byte [bp-2] ; read cl sector
int 13h ; call BIOS ISR
; try again when CF is set
jc try_again
add sp, 2
pop bp
pop di
读取的数据存在[es:bx]中,es设置成0好了,这里假定loader的大小小于64k - 5000h = 44k,所以选取bx为5000h。
<– to be continued